QUESTIONS
4:00PM
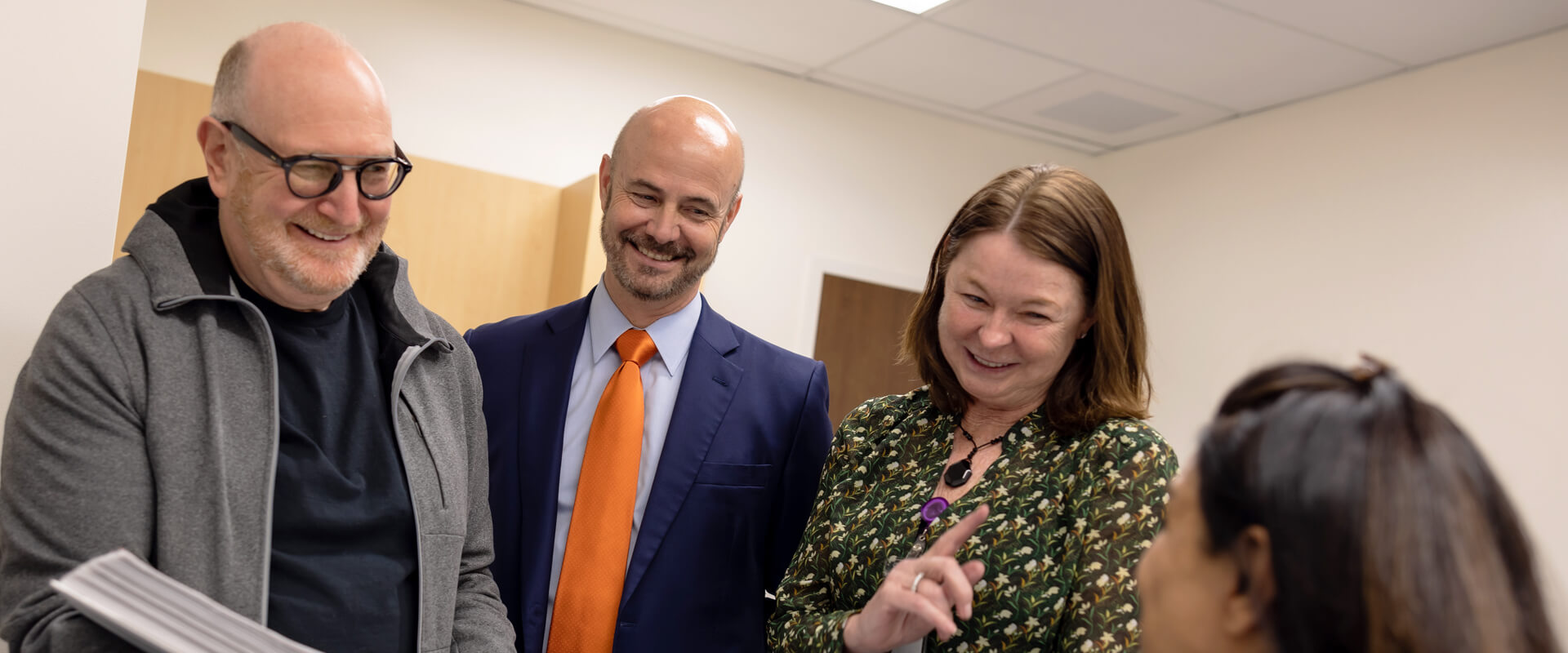
A clinical trial is a research study intended to determine if a potential new way to prevent, detect, or treat disease is safe and effective in people with a particular disease or condition. Clinical trials involving volunteer participants are the primary way that researchers evaluate whether a new drug or treatment will work and/or whether it may be more effective, or have fewer side effects, than existing drugs or treatments. According to the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), clinical trials are at the heart of all medical advances and help medical providers and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.

Clinical trials in most countries are strictly regulated by government agencies. In the U.S., clinical trials are regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), part of the federal Department of Health and Human Services. Before the FDA approves a clinical trial involving human volunteers, scientists must first perform laboratory tests and studies in animals to evaluate whether a treatment is safe and potentially effective. If these early phase trials show favorable results, the FDA can then approve human clinical trials.
Independent Review Boards (IRBs), which comprise experts in a given therapeutic area, monitor clinical trials to make sure appropriate steps are taken to protect the rights and welfare of trial participants. Under FDA regulations, an IRB has the authority to approve, require modifications in, or disapprove research. Visit the FDA website for more information on how IRBs work.
4:00PM
4:00PM
Cancer claims millions of lives around the world every year. Cancer researchers are working constantly to identify new treatments for cancer patients that will be better, more effective and/or safer than treatments that exist today. Clinical trials are a vital step in developing those treatments so they can be prescribed to patients and move us ever closer to a cure. Cancer patients who volunteer to participate in a clinical trial are not only advancing research, but also helping ensure new and better treatments are available for other cancer patients.
4:00PM
People choose to join trials for a variety of reasons. Sometimes they do so because the treatments they have tried for their health problem did not work, or did not produce an acceptable outcome. Other times, there may be no treatment currently available for their health problem. Many trial participants join trials because they want to play a more active role in their own healthcare, or because they want to help researchers learn more about certain health problems. Regardless of their reasons, patients who volunteer to participate in clinical trials may learn about new treatments months or years before they become widely available. The NIH has valuable resources for people considering joining clinical trials.
4:00PM
Most clinical trials in the United States (and globally) are listed in a database maintained by the National Library of Medicine, and available at the clinicaltrials.gov website. Individuals can search that site by disease or condition, or in other ways, to locate clinical trials of potential interest to them and learn how they or their doctors can contact the researchers in charge of the study. If you are interested in participating in one of ImmunityBio’s clinical trials, it is easy to apply: Simply complete the patient form on our website and a member of our team or a trial partner will follow up with you.
State-of-the-art diagnosis and treatment options for cancer patients
Our immune-oncology drugs, access to clinical trials, and partnerships with leading research institutions.

Our immune-oncology drugs, access to clinical trials, and partnerships with leading research institutions.

2040 East Mariposa Avenue
El Segundo, California 90245
Phone: 213-266-5600
Fax: 562-548-2304
1-855-797-9277 | info@CSSIFM.org
© 2025 CSSIFM. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Terms of Service | Notice of Privacy Practices